Minimally Invasive Gynecological Surgery
Currently, surgical treatment for gynecological diseases is often performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic procedures. Additionally, this approach involves minimal trauma, resulting in small incisions that cause less pain. It is easy to care for, facilitates quick healing, and reduces the risk of complications, leading to short hospitalization and rapid recovery. Patients can walk and resume normal activities within one day after surgery and regain independence in their daily lives quickly.
 Dr. Patraporn Tangkiratichai, our obstetrician-gynecologist and reproductive medicine specialist at Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin shares that laparoscopic surgery provides better details than traditional or open abdominal surgery because the camera used in the procedure can magnify images beyond what the naked eye can see. It aids in diagnosing gynecological conditions that may not be evident through physical examinations, CT scans, or MRIs. Additionally, it allows for both diagnosis and treatment during the same procedure.
Moreover, laparoscopic surgery reduces the need for strong post-operative pain medications. Once the patient feels well and is not experiencing nausea and vomiting, they can consume soft food and take regular painkillers. It is considered safer than open abdominal surgery, with less blood loss in some patients with a lower risk of postoperative blood transfusions. Infections and complications related to incisions are also less common. Additionally, for unmarried or women without children, laparoscopic surgery is a viable treatment option.
Dr. Patraporn Tangkiratichai, our obstetrician-gynecologist and reproductive medicine specialist at Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin shares that laparoscopic surgery provides better details than traditional or open abdominal surgery because the camera used in the procedure can magnify images beyond what the naked eye can see. It aids in diagnosing gynecological conditions that may not be evident through physical examinations, CT scans, or MRIs. Additionally, it allows for both diagnosis and treatment during the same procedure.
Moreover, laparoscopic surgery reduces the need for strong post-operative pain medications. Once the patient feels well and is not experiencing nausea and vomiting, they can consume soft food and take regular painkillers. It is considered safer than open abdominal surgery, with less blood loss in some patients with a lower risk of postoperative blood transfusions. Infections and complications related to incisions are also less common. Additionally, for unmarried or women without children, laparoscopic surgery is a viable treatment option.
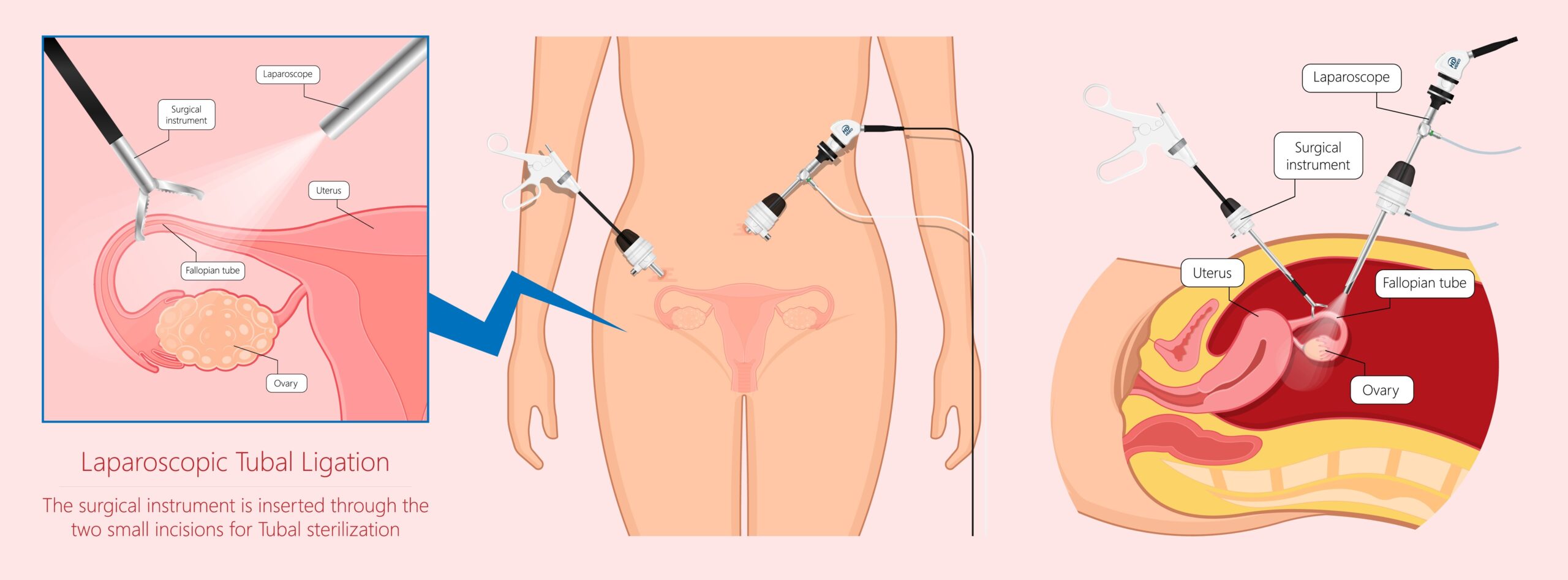 Laparoscopic Surgery Procedure
Patients undergo surgery with general anesthesia and assisted ventilation through a breathing tube administered by an anesthesiologist. In laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity. Specialized surgical tools, including a video camera, are inserted through 2-4 small incisions, each 5-10 millimeters in diameter. The video camera captures high-resolution images of the abdominal organs, which are transmitted to a television screen. The gynecologist then utilizes various instruments to perform the procedure, such as removing the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes.
Gynecological Conditions Suitable for Laparoscopic Surgery
Conditions that can be treated with laparoscopic surgery include ovarian cysts, certain types of fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal growth of uterine muscles, displaced fallopian tube tissue, chronic pelvic pain of unknown cause, pelvic organ prolapse, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and certain types of gynecological cancers, such as early-stage cervical cancer.
Differences Between Hysteroscopic Surgery and Abdominal Laparoscopy
Hysteroscopic surgery in the uterine cavity can specifically address conditions within the uterine cavity, such as uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, or localized growths. The gynecologist inserts a camera through the vaginal canal, introduces saline into the uterine cavity, and performs the surgery. This approach has no abdominal incisions, and recovery is typically quick, with most patients being able to return home after just one day of hospital stay.
Laparoscopic Surgery Procedure
Patients undergo surgery with general anesthesia and assisted ventilation through a breathing tube administered by an anesthesiologist. In laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity. Specialized surgical tools, including a video camera, are inserted through 2-4 small incisions, each 5-10 millimeters in diameter. The video camera captures high-resolution images of the abdominal organs, which are transmitted to a television screen. The gynecologist then utilizes various instruments to perform the procedure, such as removing the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes.
Gynecological Conditions Suitable for Laparoscopic Surgery
Conditions that can be treated with laparoscopic surgery include ovarian cysts, certain types of fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal growth of uterine muscles, displaced fallopian tube tissue, chronic pelvic pain of unknown cause, pelvic organ prolapse, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and certain types of gynecological cancers, such as early-stage cervical cancer.
Differences Between Hysteroscopic Surgery and Abdominal Laparoscopy
Hysteroscopic surgery in the uterine cavity can specifically address conditions within the uterine cavity, such as uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, or localized growths. The gynecologist inserts a camera through the vaginal canal, introduces saline into the uterine cavity, and performs the surgery. This approach has no abdominal incisions, and recovery is typically quick, with most patients being able to return home after just one day of hospital stay.
 Limitations of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery may not be suitable for every patient, such as those with large tumors, certain types of gynecological cancers, chronic conditions like severe lung or heart diseases, significant abdominal or pelvic adhesion, a history of serious abdominal or pelvic infections, or multiple abdominal surgeries. In some cases, open abdominal surgery may be necessary if the disease is severe or if laparoscopic tools cannot reach required areas.
After surgery, patients may experience mild shoulder pain resembling muscle soreness due to carbon dioxide gas used in the abdominal cavity. This discomfort can be alleviated with pain medication and typically resolves within 1-2 days after the surgery.
Limitations of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery may not be suitable for every patient, such as those with large tumors, certain types of gynecological cancers, chronic conditions like severe lung or heart diseases, significant abdominal or pelvic adhesion, a history of serious abdominal or pelvic infections, or multiple abdominal surgeries. In some cases, open abdominal surgery may be necessary if the disease is severe or if laparoscopic tools cannot reach required areas.
After surgery, patients may experience mild shoulder pain resembling muscle soreness due to carbon dioxide gas used in the abdominal cavity. This discomfort can be alleviated with pain medication and typically resolves within 1-2 days after the surgery.
 “The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include small incisions, minimal pain, and quick recovery. Gynecologists conduct detailed diagnostics and choose appropriate treatment for patients. They also provide information, explaining the pros and cons of surgery, along with potential risks. Preparations involve joint planning, laboratory assessments, geriatric risk evaluations, preoperative preparations, and tailored surgical plans for optimal outcomes for the patients.” Dr. Patraporn concluded.
**************************************************************************
For more information and booking an appointment, please contact :
Tel. 032-616-800 Call Center, Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin
Tel: 032-616-884 (8.00 – 17.00 hrs.) OBGYN Department, 3rd floor
News & Information >> Line ID : @bangkokhuahin
“The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include small incisions, minimal pain, and quick recovery. Gynecologists conduct detailed diagnostics and choose appropriate treatment for patients. They also provide information, explaining the pros and cons of surgery, along with potential risks. Preparations involve joint planning, laboratory assessments, geriatric risk evaluations, preoperative preparations, and tailored surgical plans for optimal outcomes for the patients.” Dr. Patraporn concluded.
**************************************************************************
For more information and booking an appointment, please contact :
Tel. 032-616-800 Call Center, Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin
Tel: 032-616-884 (8.00 – 17.00 hrs.) OBGYN Department, 3rd floor
News & Information >> Line ID : @bangkokhuahin
 Dr. Patraporn Tangkiratichai, our obstetrician-gynecologist and reproductive medicine specialist at Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin shares that laparoscopic surgery provides better details than traditional or open abdominal surgery because the camera used in the procedure can magnify images beyond what the naked eye can see. It aids in diagnosing gynecological conditions that may not be evident through physical examinations, CT scans, or MRIs. Additionally, it allows for both diagnosis and treatment during the same procedure.
Moreover, laparoscopic surgery reduces the need for strong post-operative pain medications. Once the patient feels well and is not experiencing nausea and vomiting, they can consume soft food and take regular painkillers. It is considered safer than open abdominal surgery, with less blood loss in some patients with a lower risk of postoperative blood transfusions. Infections and complications related to incisions are also less common. Additionally, for unmarried or women without children, laparoscopic surgery is a viable treatment option.
Dr. Patraporn Tangkiratichai, our obstetrician-gynecologist and reproductive medicine specialist at Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin shares that laparoscopic surgery provides better details than traditional or open abdominal surgery because the camera used in the procedure can magnify images beyond what the naked eye can see. It aids in diagnosing gynecological conditions that may not be evident through physical examinations, CT scans, or MRIs. Additionally, it allows for both diagnosis and treatment during the same procedure.
Moreover, laparoscopic surgery reduces the need for strong post-operative pain medications. Once the patient feels well and is not experiencing nausea and vomiting, they can consume soft food and take regular painkillers. It is considered safer than open abdominal surgery, with less blood loss in some patients with a lower risk of postoperative blood transfusions. Infections and complications related to incisions are also less common. Additionally, for unmarried or women without children, laparoscopic surgery is a viable treatment option.
 Laparoscopic Surgery Procedure
Patients undergo surgery with general anesthesia and assisted ventilation through a breathing tube administered by an anesthesiologist. In laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity. Specialized surgical tools, including a video camera, are inserted through 2-4 small incisions, each 5-10 millimeters in diameter. The video camera captures high-resolution images of the abdominal organs, which are transmitted to a television screen. The gynecologist then utilizes various instruments to perform the procedure, such as removing the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes.
Gynecological Conditions Suitable for Laparoscopic Surgery
Conditions that can be treated with laparoscopic surgery include ovarian cysts, certain types of fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal growth of uterine muscles, displaced fallopian tube tissue, chronic pelvic pain of unknown cause, pelvic organ prolapse, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and certain types of gynecological cancers, such as early-stage cervical cancer.
Differences Between Hysteroscopic Surgery and Abdominal Laparoscopy
Hysteroscopic surgery in the uterine cavity can specifically address conditions within the uterine cavity, such as uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, or localized growths. The gynecologist inserts a camera through the vaginal canal, introduces saline into the uterine cavity, and performs the surgery. This approach has no abdominal incisions, and recovery is typically quick, with most patients being able to return home after just one day of hospital stay.
Laparoscopic Surgery Procedure
Patients undergo surgery with general anesthesia and assisted ventilation through a breathing tube administered by an anesthesiologist. In laparoscopic surgery, carbon dioxide gas is introduced into the abdominal cavity. Specialized surgical tools, including a video camera, are inserted through 2-4 small incisions, each 5-10 millimeters in diameter. The video camera captures high-resolution images of the abdominal organs, which are transmitted to a television screen. The gynecologist then utilizes various instruments to perform the procedure, such as removing the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes.
Gynecological Conditions Suitable for Laparoscopic Surgery
Conditions that can be treated with laparoscopic surgery include ovarian cysts, certain types of fibroids, endometriosis, abnormal growth of uterine muscles, displaced fallopian tube tissue, chronic pelvic pain of unknown cause, pelvic organ prolapse, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, and certain types of gynecological cancers, such as early-stage cervical cancer.
Differences Between Hysteroscopic Surgery and Abdominal Laparoscopy
Hysteroscopic surgery in the uterine cavity can specifically address conditions within the uterine cavity, such as uterine fibroids, endometrial polyps, or localized growths. The gynecologist inserts a camera through the vaginal canal, introduces saline into the uterine cavity, and performs the surgery. This approach has no abdominal incisions, and recovery is typically quick, with most patients being able to return home after just one day of hospital stay.
 Limitations of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery may not be suitable for every patient, such as those with large tumors, certain types of gynecological cancers, chronic conditions like severe lung or heart diseases, significant abdominal or pelvic adhesion, a history of serious abdominal or pelvic infections, or multiple abdominal surgeries. In some cases, open abdominal surgery may be necessary if the disease is severe or if laparoscopic tools cannot reach required areas.
After surgery, patients may experience mild shoulder pain resembling muscle soreness due to carbon dioxide gas used in the abdominal cavity. This discomfort can be alleviated with pain medication and typically resolves within 1-2 days after the surgery.
Limitations of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery may not be suitable for every patient, such as those with large tumors, certain types of gynecological cancers, chronic conditions like severe lung or heart diseases, significant abdominal or pelvic adhesion, a history of serious abdominal or pelvic infections, or multiple abdominal surgeries. In some cases, open abdominal surgery may be necessary if the disease is severe or if laparoscopic tools cannot reach required areas.
After surgery, patients may experience mild shoulder pain resembling muscle soreness due to carbon dioxide gas used in the abdominal cavity. This discomfort can be alleviated with pain medication and typically resolves within 1-2 days after the surgery.
 “The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include small incisions, minimal pain, and quick recovery. Gynecologists conduct detailed diagnostics and choose appropriate treatment for patients. They also provide information, explaining the pros and cons of surgery, along with potential risks. Preparations involve joint planning, laboratory assessments, geriatric risk evaluations, preoperative preparations, and tailored surgical plans for optimal outcomes for the patients.” Dr. Patraporn concluded.
**************************************************************************
For more information and booking an appointment, please contact :
Tel. 032-616-800 Call Center, Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin
Tel: 032-616-884 (8.00 – 17.00 hrs.) OBGYN Department, 3rd floor
News & Information >> Line ID : @bangkokhuahin
“The advantages of laparoscopic surgery include small incisions, minimal pain, and quick recovery. Gynecologists conduct detailed diagnostics and choose appropriate treatment for patients. They also provide information, explaining the pros and cons of surgery, along with potential risks. Preparations involve joint planning, laboratory assessments, geriatric risk evaluations, preoperative preparations, and tailored surgical plans for optimal outcomes for the patients.” Dr. Patraporn concluded.
**************************************************************************
For more information and booking an appointment, please contact :
Tel. 032-616-800 Call Center, Bangkok Hospital Hua Hin
Tel: 032-616-884 (8.00 – 17.00 hrs.) OBGYN Department, 3rd floor
News & Information >> Line ID : @bangkokhuahin